Latest Reserach Posts
Recharging the powerhouse of the cell
Researchers at Texas A&M University have developed a method to rejuvenate old and damaged human cells by replacing their mitochondria.
Cleveland Clinic First-In-Human Trial of CRISPR Gene-Editing Therapy Shown to Safely Lower Cholesterol and Triglycerides
One-time infusion of investigational CRISPR-Cas9 therapy found to safely reduce LDL cholesterol by 50% and triglycerides by about 55% in Phase 1 trial
Particles that enhance mRNA delivery could reduce vaccine dosage and costs
Using these nanoparticles to deliver a flu vaccine, researchers observed an effective immune response at a much lower dose.

Brain-to-Brain Similarity Predicted Who People Became Friends With Before They Even Met
What pushes an acquaintance into friendship territory? While there are plenty of reasons we forge bonds with others — proximity, shared hobbies, similar values — new research from the University of California Los Angeles and Dartmouth College suggests a neurological explanation for kinship as well.
Scientists discover how to wipe out breast cancer’s hidden cells
Clinical trial offers proof-of-concept for a treatment approach to prevent breast cancer recurrence.
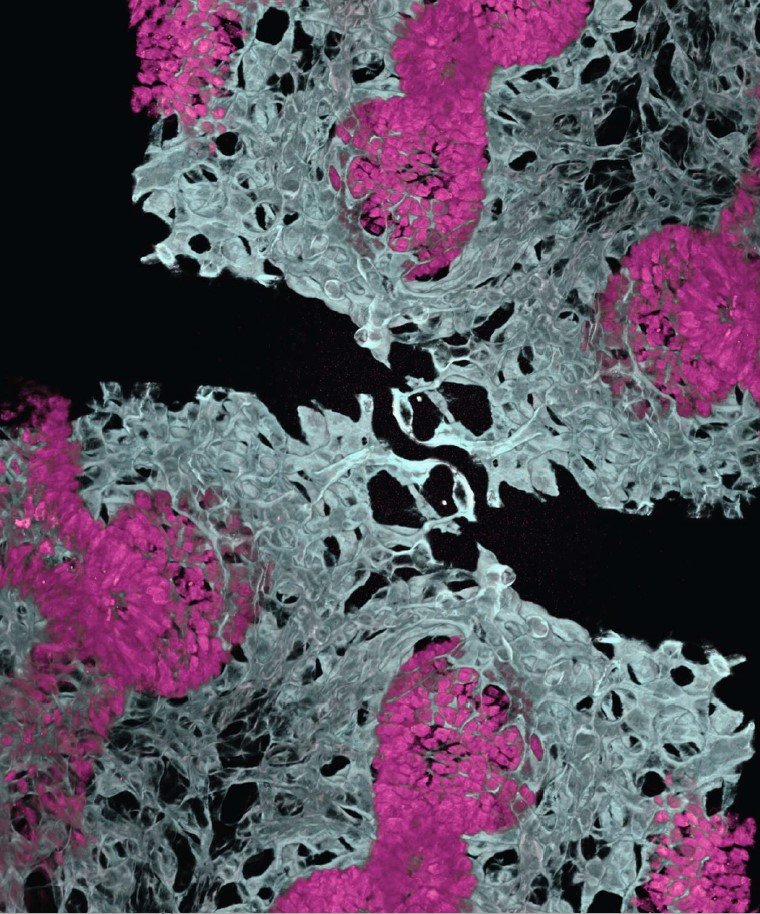
Scientists create organoids with specialized blood vessels
Scientists made mini-lungs and intestines, called organoids, that generate their own specialized blood vessels.
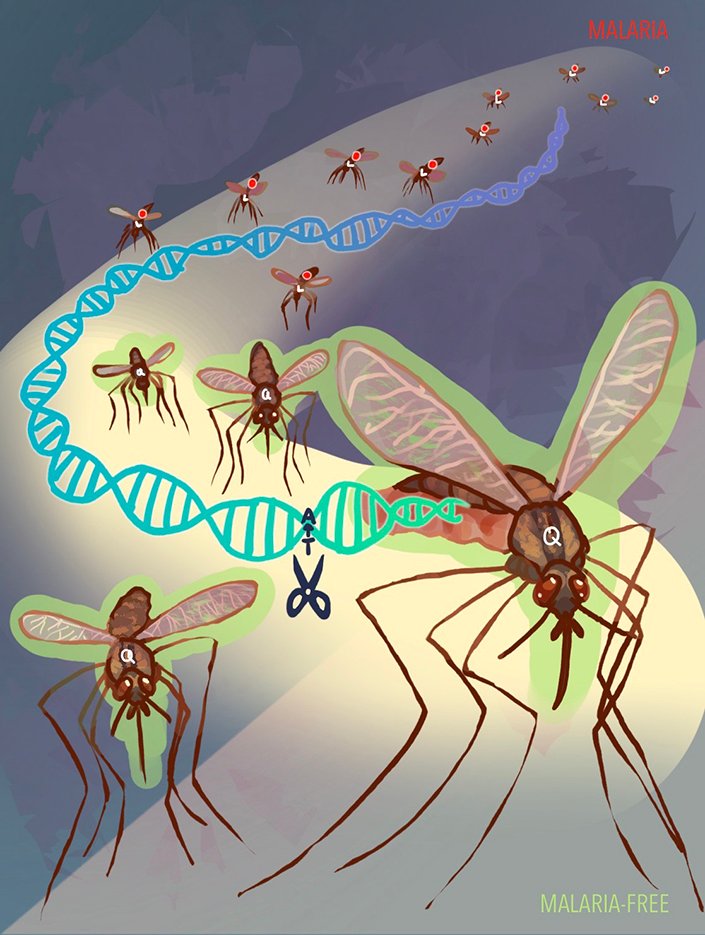
Stealth Genetic Switch in Mosquitoes Halts Malaria Spread
Researchers have developed a new method that genetically blocks mosquitoes from transmitting malaria. The study was published July 23, 2025 in the journal Nature.

Mitochondria and health
Your cells’ mitochondria produce almost all the energy your body needs to survive. They also play a role in many other vital cellular functions. This Research in Context feature looks at how insights about these cellular powerhouses might lead to new ways of preventing and treating disease.
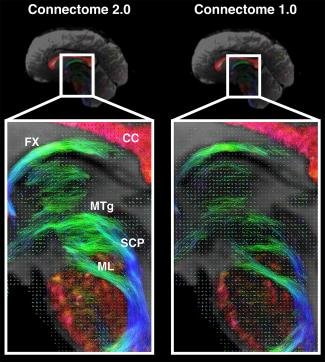
Scientists Develop High-Performance MRI Scanner in Effort to Define Microscopic Brain Structures
Next-generation system noninvasively images tiny nerve structures disrupted in brain disorders.
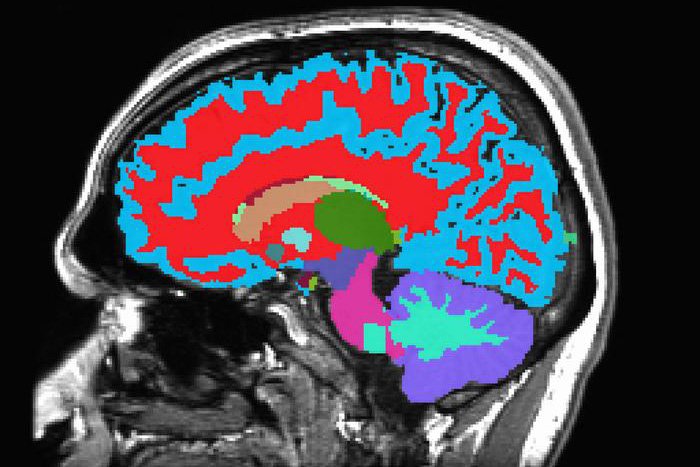
Measuring aging with brain scans
Researchers developed a way to measure how fast a person is aging from a single brain scan.